When it comes to welding in manufacturing, we always have two primary options - robotic welding or traditional manual welding. Both approaches have their own unique advantages and disadvantages. Which one provides greater efficiency in welding?
Manual Welding
Advantages of Manual Welding
- Flexibility: Human welders can more easily adapt to changes in part designs, materials, and welding specifications compared to pre-programmed robots.
- Upfront Costs: The initial investment in manual welding equipment and tools is typically less than the cost of a robotic welding cell.
Limitations of Manual Welding
- Speed & Throughput: Manual welders have physical limitations in terms of maximum welding output per hour, with performance degrading over long shifts due to fatigue.
- Efficiency: Hardly two parts will be produced by one manual welder with the same level of precision.
- Consistency & Quality: Even the most skilled manual welders will produce some degree of variability in weld quality.
- Labor Costs: Manual welding requires a one-to-one ratio of welder to workstation, leading to greater direct labor expenses.
Robotic Welding
Advantages of Robotic Welding
- Speed & Throughput: Robotic welding services can perform welds at a much faster rate compared to human welders. Robots can work continuously without breaks, leading to higher output per hour.
- Efficiency: Robots can weld faster and more efficiently than manual welding, allowing them to meet customer demands and shorten project timelines. The no-programming approach is effective even for small tasks, making robot teaching and deployment quicker than manual welding.
- Consistency & Quality: Robotic welding movements are precisely programmed and repeatable, resulting in higher weld quality and lower defect rates compared to manual welding.
- Labor Costs: A single operator can manage multiple robotic welding cells simultaneously, significantly lowering the direct labor required.
Limitations of Robotics Welding
- Upfront Investment: The capital cost of purchasing and installing a robotic welding machine is generally higher than the equipment needed for manual welding.
- Flexibility: Robotic welding is best suited for high-volume, repetitive welding tasks with minimal variation in part size, geometry, and welding requirements. Adapting to new products or small batches can be more challenging.
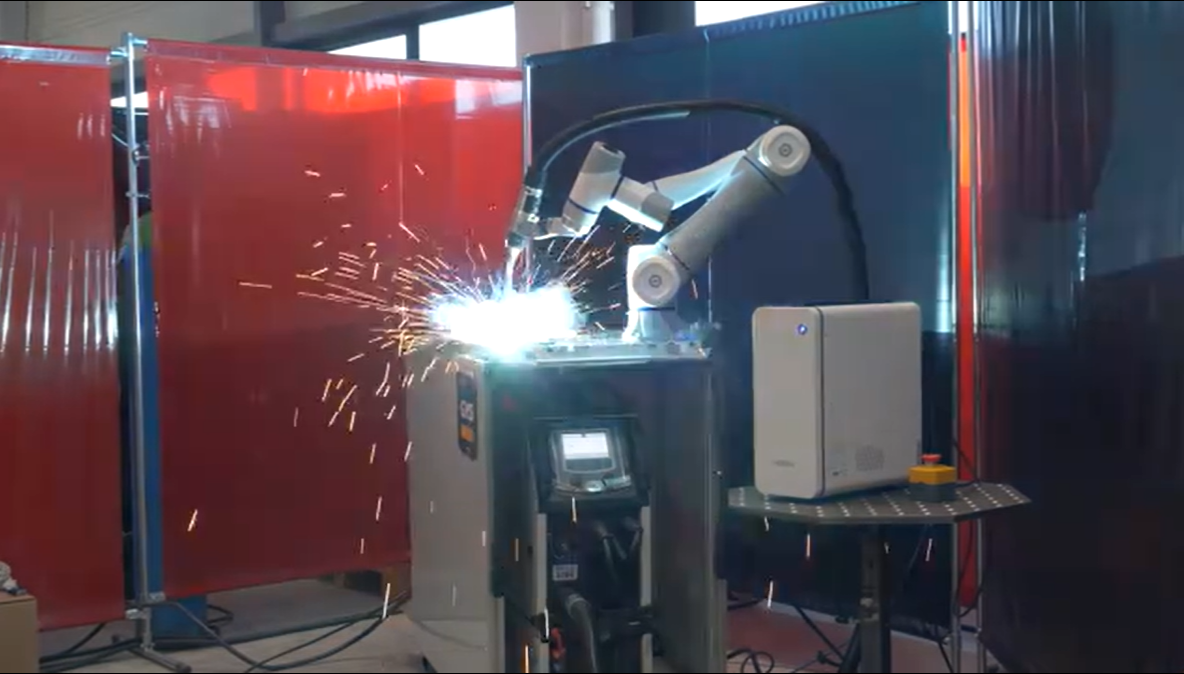

Dobot CR Series Cobot Welding on Carbon Steel Fillet
In summary, while both robotic welding and manual welding have their place in manufacturing, the data generally shows that robotic welding provides greater overall efficiency, especially for high-volume production environments. The speed, consistency, and labor savings of robotic systems tend to outweigh the flexibility and lower upfront costs of manual welding. However, businesses should carefully evaluate their specific requirements and constraints to determine the optimal welding approach.