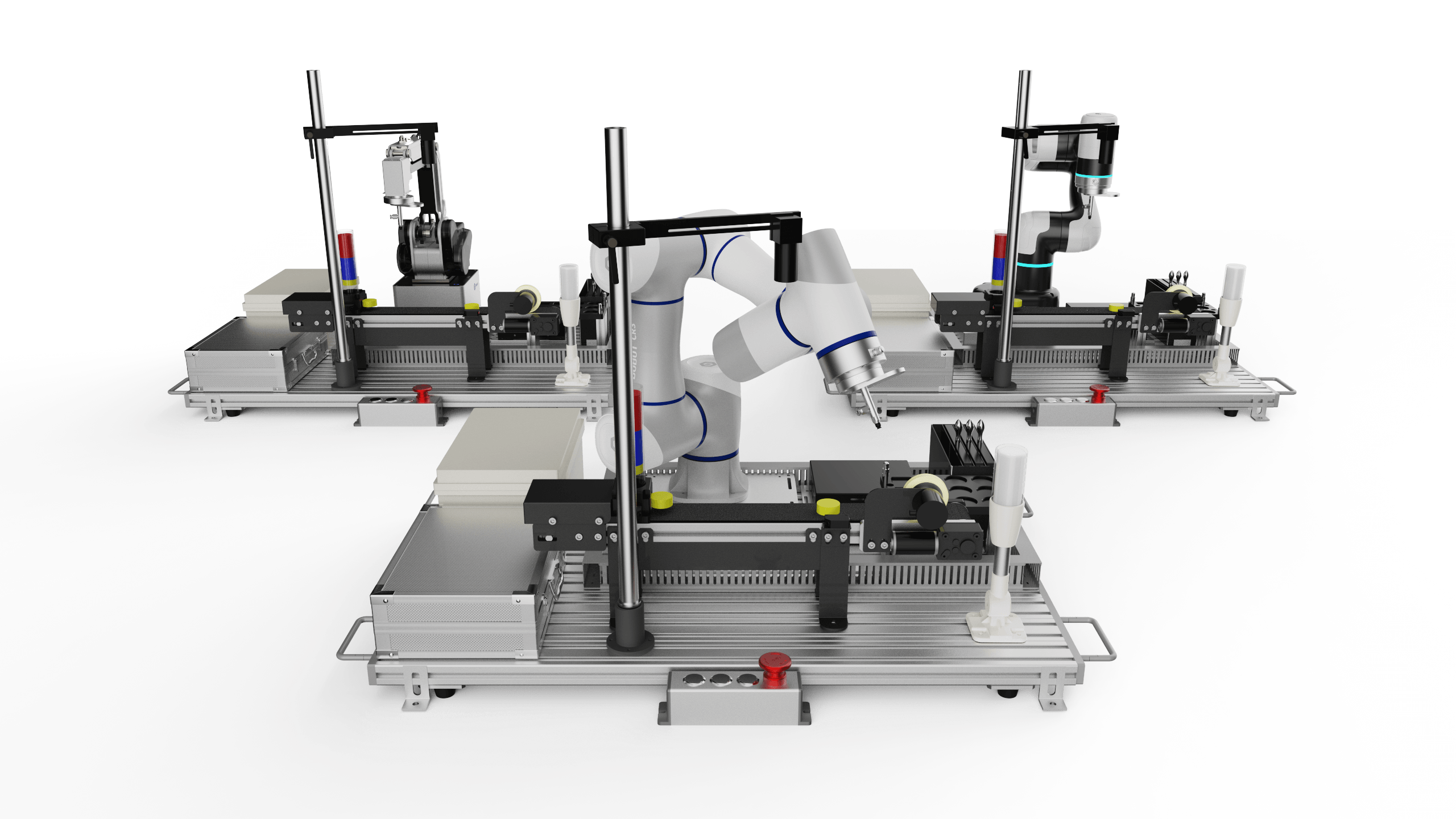
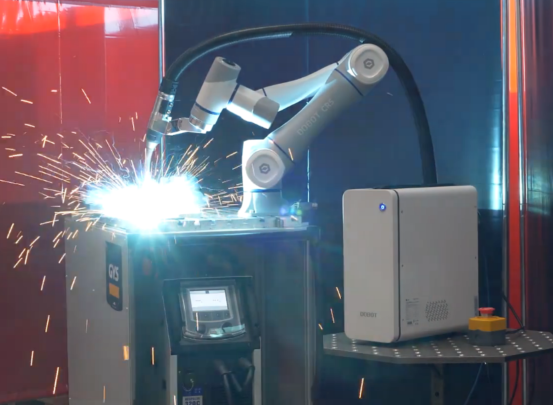
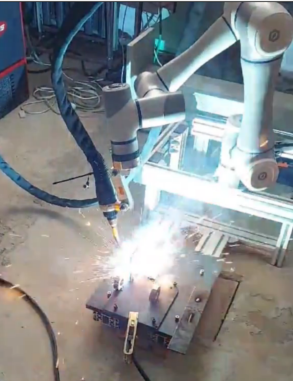
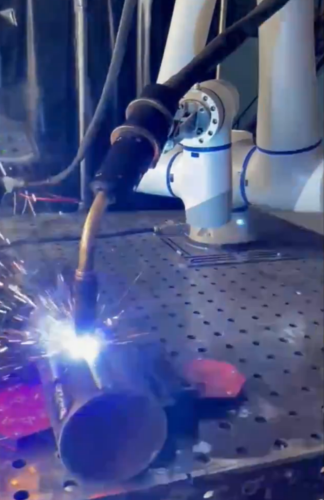
-
Download CenterGet the latest software and firmware to keep your robots up to date.
-
Academy serviceLevel up your automation with robotics training sessions.
-
Customer ServiceGet dedicated support you need to optimize Dobot robots.
-
FAQCommon questions answered here.